January 1, 2019
by Mikhail Elyashberg, Leading Researcher, ACD/Labs
Rhodomollacetal A
Grayanane and several related diterpenoids can be found in Rhododendron molle. They feature a unique 5/7/6/5 tetracyclic skeleton, existing exclusively in the Ericeceae plants. These compounds have been found to have significant bioactivity. Consequently the total synthesis of these complex, highly oxygenated polycyclic structures has attracted considerable attention in the organic synthesis community.
Zhou et al [1] isolated three novel diterpenoids with an unprecedented 2,3:5,6-di-seco-grayanane carbon skeleton, rhodomollacetals A−C. Rhodomollacetal A, compound 1, possesses a novel cis/cis/cis/cis-fused 6/6/6/6/5 pentacyclic system, featuring an unprecedented 11,13,18-trioxa-pentacyclo[8.7.1.15,8.02,8.012,17]nonadecane scaffold.
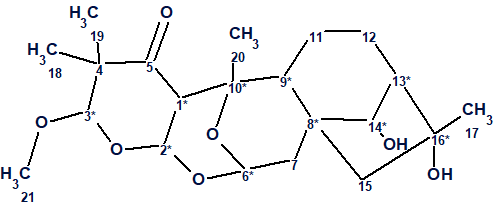
1
Its structure was elucidated in [1] by spectroscopic techniques (NMR and IR) and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The spectroscopic data used to elucidate the structure of Rhodomollacetal A were used to challenging ACD/Structure Elucidator.
Rhodomollacetal A (1) was obtained as colorless prisms, mp 167−168 °C. The molecular formula of 1 was determined as C21H32O7 by the HR-ESI-MS ion at m/z 419.2051 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C21H32O7Na, 419.2046) and 13C NMR data, indicating six degrees of unsaturation. The IR spectrum shows the presence of hydroxy (3408 cm−1) and ketone (1704 cm−1) groups in 1. 1D and 2D NMR data of compound 1 are presented in Table 1. Only 1H and 13C chemical shifts were tabulated in [1], while key HMBC and COSY correlations were mapped by arrows on the structure.
Table 1. 1H, 13C, HSQC, HMBC and COSY data of Rhodomollacetal A.
| Label | δC | δC calc (HOSE) | CHn | δH | COSY | H to C HMBC |
| C 1 | 59.400 | 55.320 | CH | 2.730 | 5.62 | C 4 |
| C 2 | 91.300 | 93.920 | CH | 5.620 | 2.73 | C 10, C 3 |
| C 3 | 106.300 | 105.670 | CH | 4.570 | ||
| C 4 | 51.700 | 50.810 | C | |||
| C 5 | 210.900 | 214.820 | C | |||
| C 6 | 94.700 | 93.060 | CH | 5.470 | 1.50 | C 10, C 2 |
| C 7 | 34.300 | 42.930 | CH2 | 1.500 | 5.47 | C 8, C 9 |
| C 7 | 34.300 | 42.930 | CH2 | 2.780 | ||
| C 8 | 48.100 | 45.890 | C | |||
| C 9 | 50.700 | 46.950 | CH | 2.380 | 1.62 | C 8 |
| C 10 | 76.800 | 80.150 | C | |||
| C 11 | 19.800 | 21.090 | CH2 | 1.550 | ||
| C 11 | 19.800 | 21.090 | CH2 | 1.620 | 1.72, 2.38 | |
| C 12 | 27.400 | 25.920 | CH2 | 1.720 | 1.62, 2.03 | |
| C 12 | 27.400 | 25.920 | CH2 | 1.810 | ||
| C 13 | 54.900 | 56.150 | CH | 2.030 | 1.72, 4.11 | |
| C 14 | 79.900 | 79.360 | CH | 4.110 | 2.03 | C 8, C 9 |
| C 15 | 55.500 | 56.940 | CH2 | 1.860 | C 7, C 8, C 14 | |
| C 16 | 80.600 | 80.420 | C | |||
| C 17 | 23.600 | 23.490 | CH3 | 1.330 | C 13, C 15, C 16 | |
| C 18 | 19.700 | 20.190 | CH3 | 1.040 | C 4, C 3, C 5 | |
| C 19 | 21.700 | 21.090 | CH3 | 1.230 | C 18, C 4, C 3, C 5 | |
| C 20 | 23.700 | 23.920 | CH3 | 1.370 | C 9, C 1, C 10 | |
| C 21 | 56.900 | 57.810 | CH3 | 3.430 | C 3 |
The molecular connectivity diagram (MCD) created by the program is shown in Figure 1.
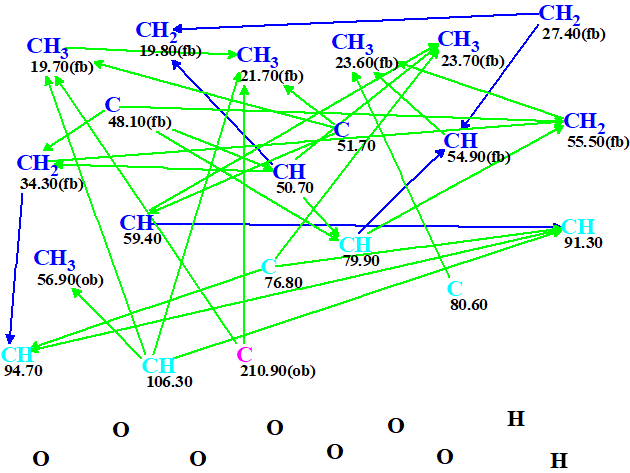
Figure 1. Molecular Connectivity Diagram. HMBC correlations are marked by green arrows, COSY correlations – by blue ones.
MCD overview. All carbon atom hybridizations and “fb” (neighboring of a heteroatom is forbidden) and “ob” (neighboring of a heteroatom is obligatory) labels were determined by the program automatically. For the six atoms (colored in light blue) the hybridization was set as ambiguous – either sp2 or sp3 (not sp). Carbon atom C 210.9 was defined as a carbonyl.
No manual edits of the MCD were done and structure generation was initiated. Result: k = 1, tg = 0.16 s, i.e., only one structure (Figure 2) was generated in 160 ms.
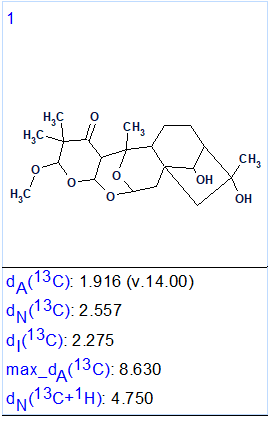
Figure 2. The single generated structure.
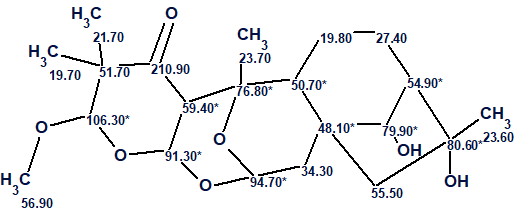
We see that the correct structure of Rhodomollacetal A was unambiguously determined by the program in a fully automatic way. The values of average deviations calculated as a result of 13C chemical shift prediction by the three approaches implemented in ACD/Structure Elucidator (HOSE code based, dA; artificial neural networks, dN; incremental approach, dI) allow concluding that the structure (confirmed by X-ray analysis) is elucidated reliably.
A single structure was obtained because of the fact that in this case, HMBC and COSY spectra delivered a lot of structural information which constrained the problem sufficiently to eliminate all other plausible structures. The size of the output file may be large enough (hundreds and thousands of structures) if a molecule is hydrogen deficient and does not contain 1H spin systems or if the problem is in another way insufficiently constrained [2].
The structure of Rhodomollacetal A, in which all HMBC (green arrows) and COSY (blue arrows) correlations are shown, is presented in Figure 3. We see that the COSY spectrum comes from the presence of three spin systems. It was interesting to see if the problem could be solved without the COSY data. For this the COSY spectrum was temporarily ignored and structure generation accompanied with 13C chemical shift prediction and structure filtering was performed using the information from the other spectra.
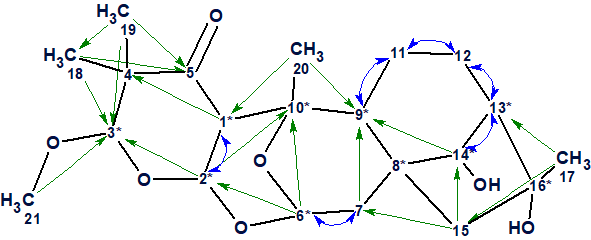
Figure 3. HMBC and COSY correlations.
Results: k = 7634→341→191, tg = 27 s. We see that excluding the COSY data led to a significant increase of the output file size, almost by a factor of 200. Then 13C chemical shift prediction was performed and the structures were ranked in accordance with the standard ACD/Structure Elucidator method. Figure 4 shows the 12 top ranked structures.
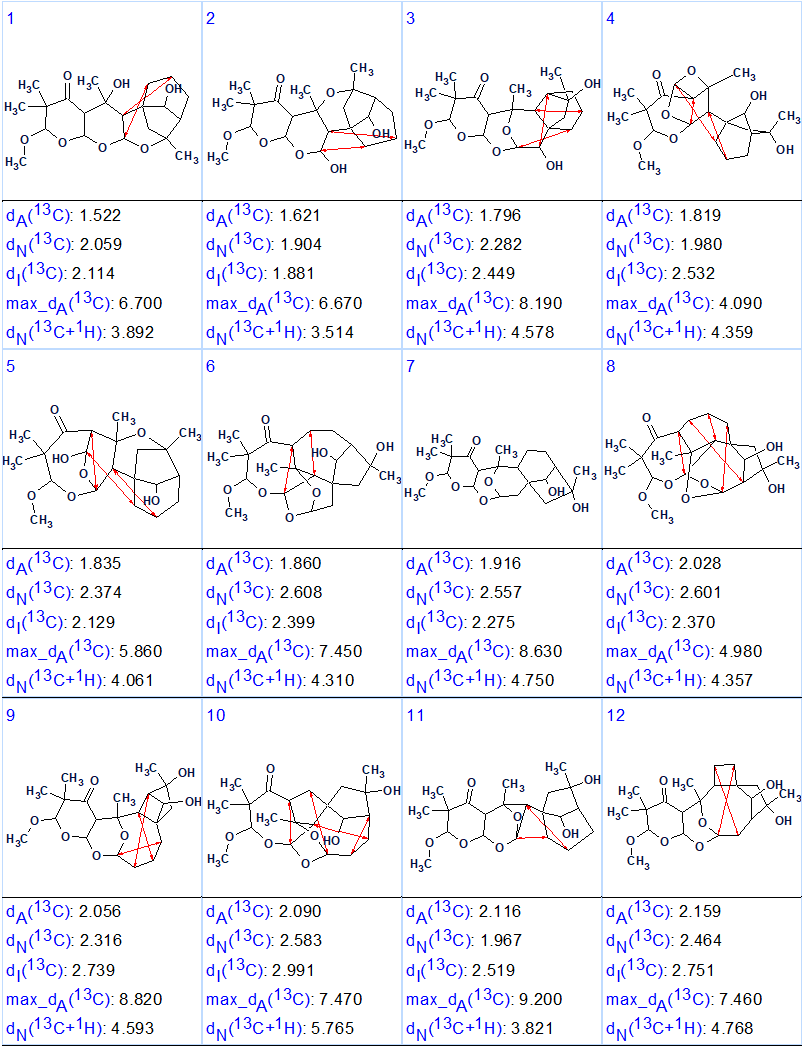
Figure 4. Top ranked structures of the output file obtained without utilization of COSY correlations.
We see that the correct structure 1 is placed in seventh position. The information from the COSY spectrum were utilized at this point to indicate the unexpected correlations for each of the 12 structures. These are indicated by the red arrows. Structure #7 is the only one where there are not unexpected (or unlikely) COSY correlations. It is evident that distinguishing the right structure among those shown in Figure 4 would be problematic without using the COSY data. In this case COSY is decisive in obtaining a single structure.
Finally, the structure of Rhodomollacetal A along with the automatically carried out 13C chemical shift assignments is shown below.
References
- J. Zhou, N. Sun, H. Zhang, G. Zheng, J. Liu, G. Yao. Rhodomollacetal A−C, PTP1B Inhibitory Diterpenoids with a 2,3:5,6-Di-seco-grayanane Skeleton from the Leaves of Rhododendron molle. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5352−5355
- M. E. Elyashberg, A. J. Williams. (2015). Computer-based Structure Elucidation from Spectral Data. The Art of Solving Problems. Springer.


