
ACD/Name (Chemist Version) offers a standardized set of features for quick and simple generation of IUPAC names, and structures from names. It is a streamlined version of our popular ACD/Name software.
View a full description and pricing on our web store.

Examples to R-1.2
Parent:
HeptaneParent: 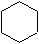
Cyclohexane
(Cyclohexane is chosen as parent because it bears the principal characteristic group -COOH, see R-4).


Published with permission of the IUPAC by Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., www.acdlabs.com, +1(416)368-3435 tel, +1(416)368-5596 fax. For comments or suggestions please contact webmaster@acdlabs.com