Version 2023 of Luminata adds new features, including peak metadata synchronization, and improves existing ones, such as adding new chemical entities. Read below for details, and contact us for help upgrading your software.
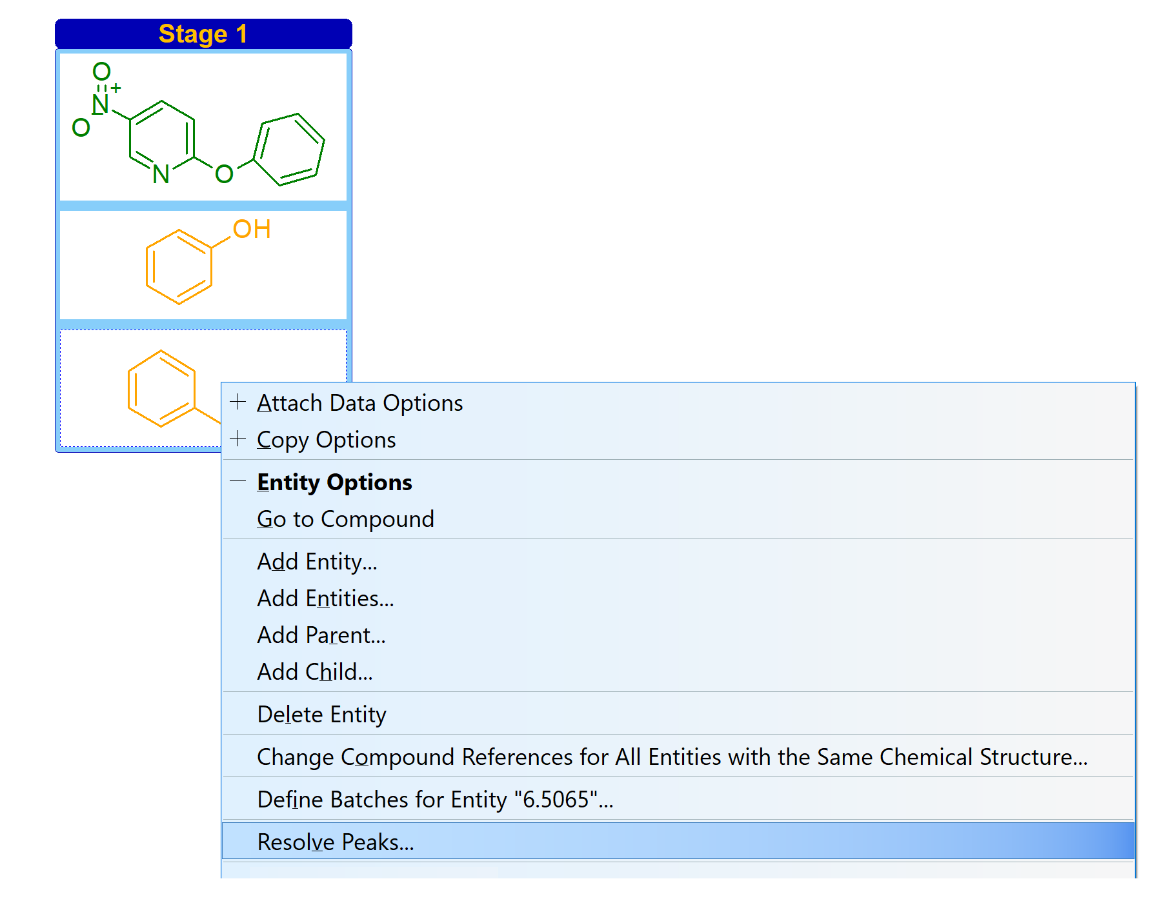
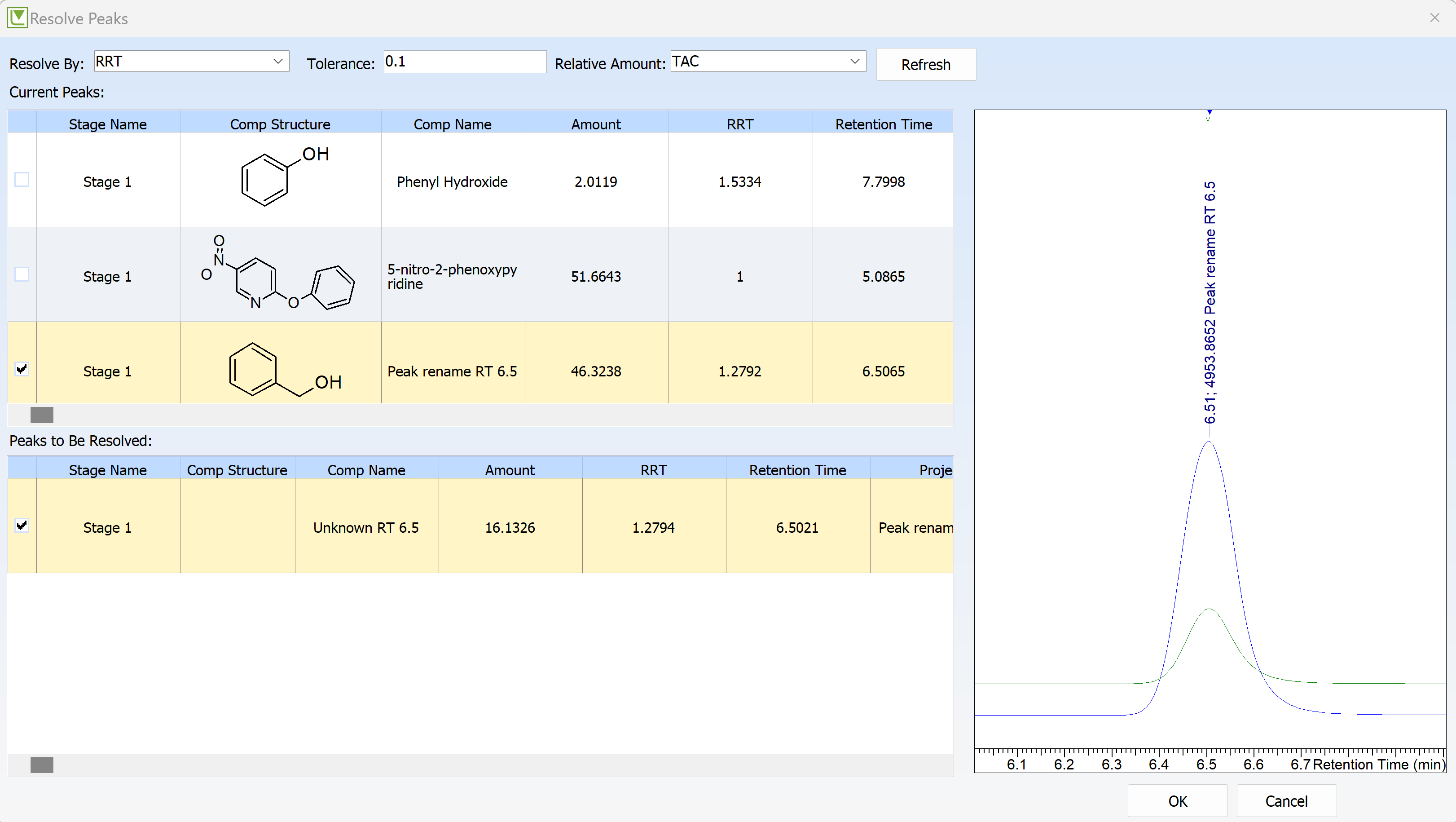
Synchronize Structures Across Associated Chromatograms
You can now add or change the compound associated with peaks at a given retention time (or relative retention time) for multiple chromatograms within the same project, process, or stage.
More Tools for Comparing Data Across Multiple Sets of Experiments
New tables and an improved Control Chart allow you to review and compare analytical results from across multiple experiments.
- You can now identify which set of conditions lead to the highest total level of impurities in the Batch Impurity Peak Amount Table
- View all the spectra or chromatograms for a selected entity, compound, or stage using the Spectra/Chromatogram Table. This is a more convenient way to review analytical data across multiple instrument and detector types; or see all the analytical data for a specific technique for a given project.
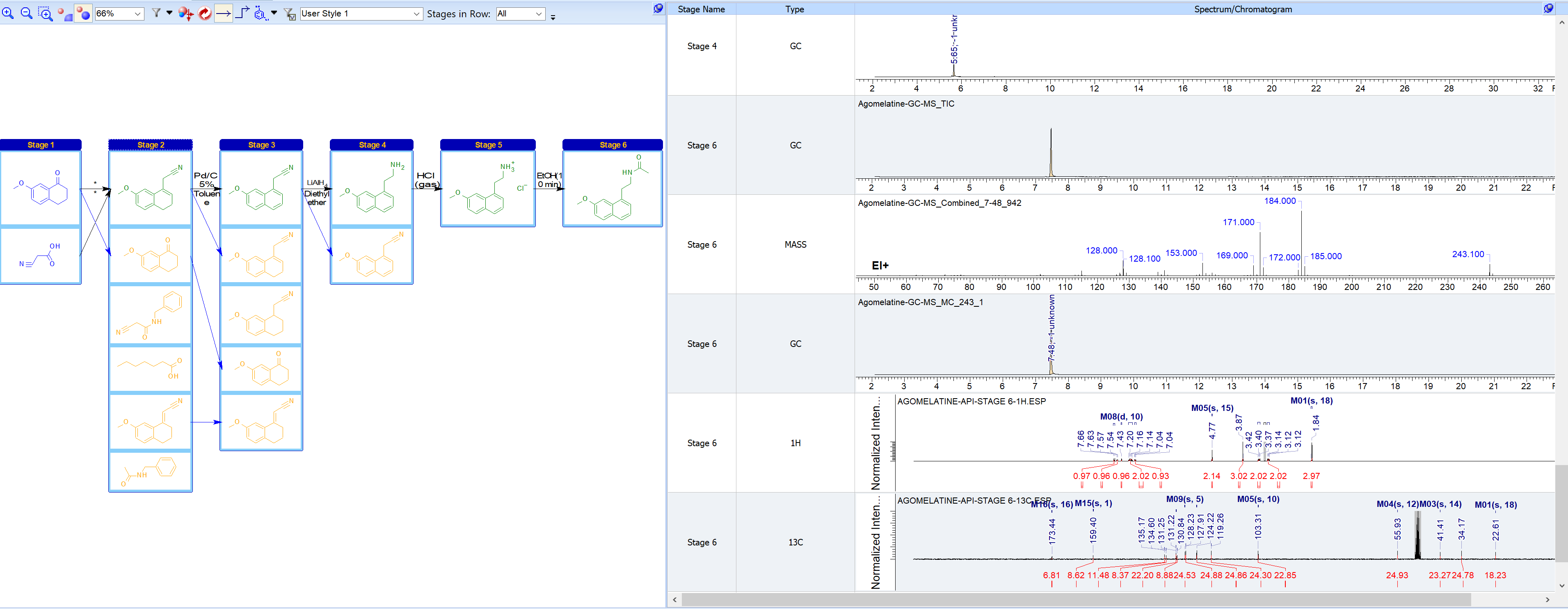 Review all your spectra/chromatograms for a given stage of a project in a table format.
Review all your spectra/chromatograms for a given stage of a project in a table format.
- You can now compare data across multiple projects in the Control chart
Greater Flexibility for Reactions in Batch Schemes and Process Maps
Solvents, reagents, and reaction conditions can now be added above or below reaction arrows within the batch scheme and process map, allowing you to review reaction conditions more easily at each step. This data is also searchable within the batch scheme, allowing you to identify all reactions that use a given solvent or temperature.
Reaction conditions have been added above and below the reaction arrow, allowing you to quickly review reaction conditions.
More Convenient Import and Addition of Chemical Entities
You can more easily add chemical entities into the software.
- Add entities to multiple stages at once
- You now have more filtering options when importing batches to a family tree, or compounds to a process map. This helps ensure imported batches are stored accurately.
- When adding a new synthetic route record, you can now confirm all entities
- Choose multiple metadata parameters to be automatically included when importing a spectrum or chromatogram
- Connect entities to a specific batch. This allows you to include information about the origin of specific starting materials or reagents.
Customized Collapsible Menus
You can now group commands within the right-click menu. Default groupings can be customized in the configuration file.
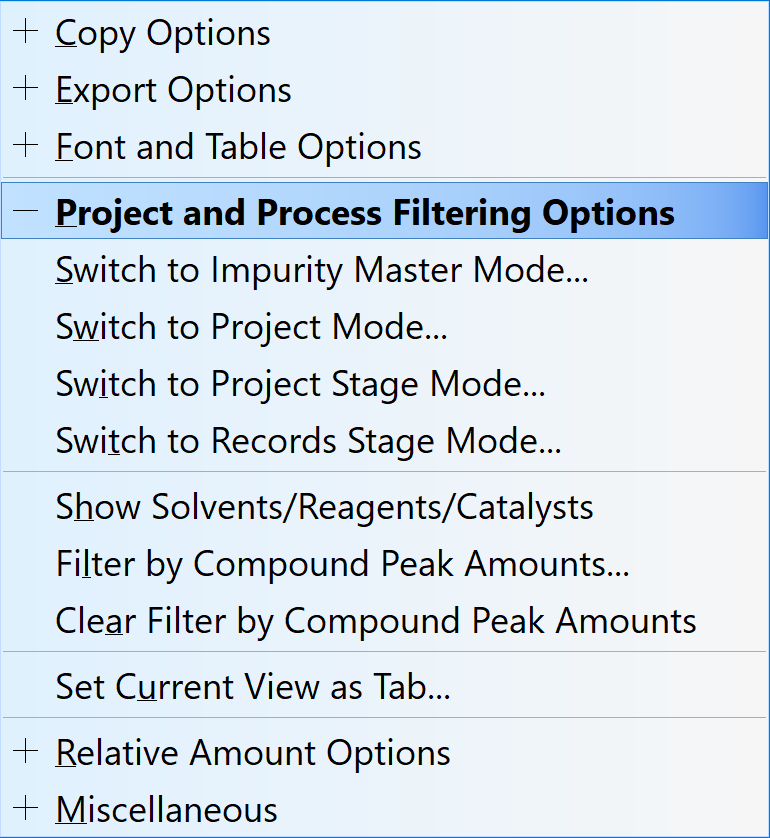
More Control When Viewing Summaries of Impurities Information
The Compounds Relations Table, which summarizes information about where impurities appear, now allows you to bring in data from a wider range of sources. It also features enhanced filtering options.
- Include data from batches, batch schemes, and reactions in the Compound Relations Table at the same time and see everywhere that a selected compound is present.
- The Compounds Relation Table can now show the % peak area for a stage, entity, or batch. This table can also be filtered, allowing you to view only impurities that are present at significant levels.
- You can now filter the Compound Relations Table to show all instances in which a specific compound is found.
Enhanced Data Management in the Control Chart
The control chart now has additional options that allow you to view your data in your preferred format, or export only selected rows.
- You can now switch between peak retention times instead of relative areas
- Calculate purge factor and carryover for compounds
- Selected rows can now be exported
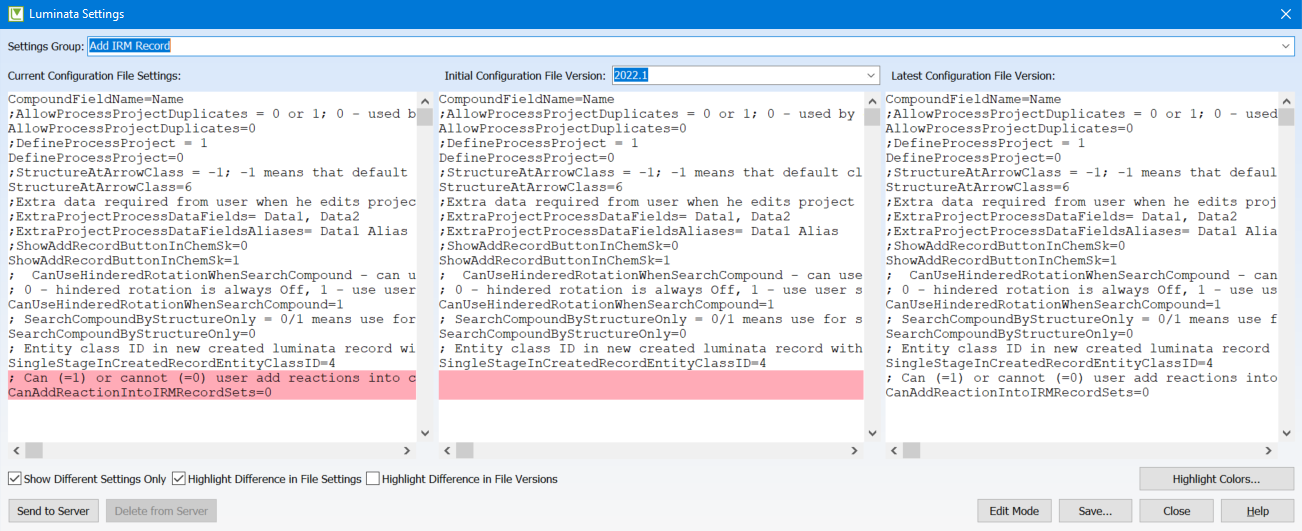
View Changes in User Settings When Configuration is Changed
You can now view any changes in user settings between the current configuration and the most recent configuration. This is helpful for system administrators to be able to ensure settings are accurate after performing an update.
Ease of Use
- View the synonyms of impurities in the Genealogy Analysis Table
- Filter the Genealogy Analysis Table, offering greater flexibility when searching for chemicals
- Hide all entities, or hide entities within a stage, to focus on the most relevant sections of a process map
- You can now import impurity structure, analytical, and metadata data from text, CSV, and SDfiles
- We improved data import from:
- Agilent OpenLab ChemStation and Bruker LC/MS ToF DAD traces—DAD data and extracted wavelengths can now be imported and viewed
- We now support Shimadzu LabSolutions CDS data from LCMS-9050 Q-TOFs
- We now support import from archives (i.e., *.zip)
- Thermo Scientific Chromeleon CDS add-on is improved to display m/z values for SIM data
- OpenLab CDS add-on now uses a single processing method to export all datasets in the OpenLab CDS repository
- We have expanded the data you can export to JSON format for use in data science and modeling
- Export hyphenated xC/UV/MS data
- Export processed 1D and 2D NMR spectra, including peaks, multiplets, and assignments
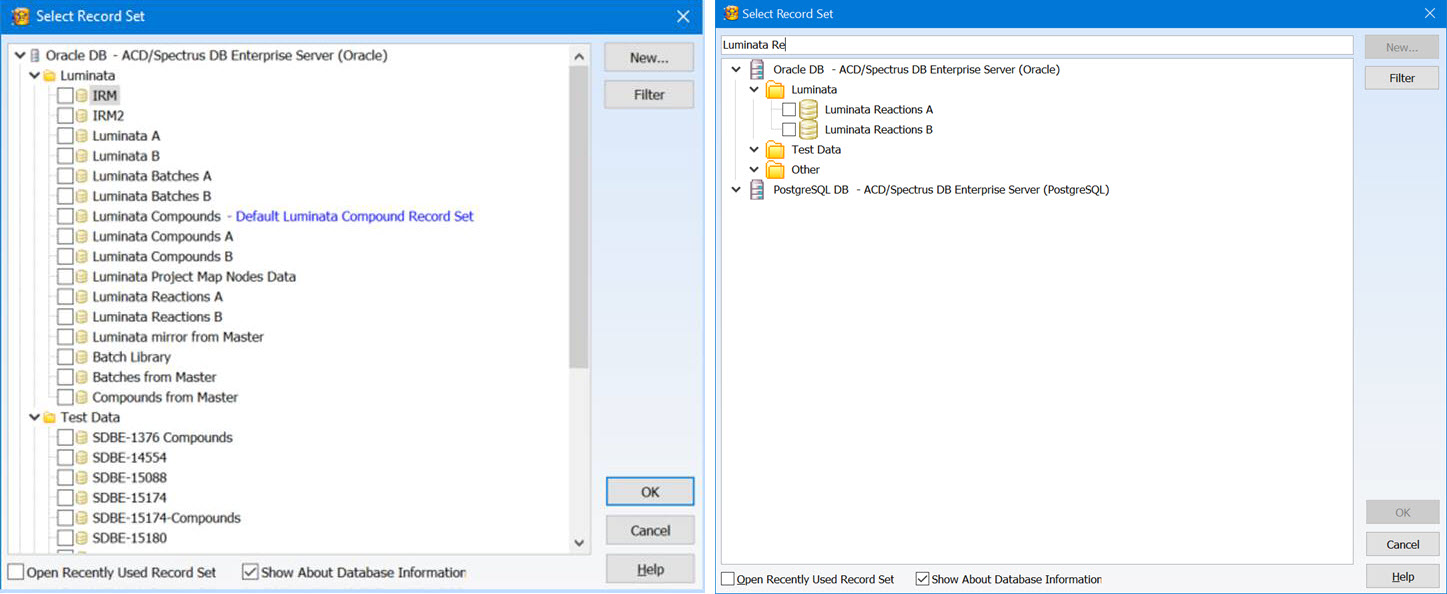
Enhanced Record Set Management
You now have additional features to help organize and review record sets, making it easier to find what you are looking for.
- Organize record sets into a tree layout using the Enterprise Server Management Console for greater control
- Add descriptive information to be displayed when you select a record set
- Text search is now available when reviewing record sets
Permission Management
Record owners can no longer open record sets by default. These permissions can be edited by a system administrator.
Expanded Database Search Options
You now have more tools for finding the data you need within database records.
- Search for records where a given table exists or not
- Common mass spectrometry related queries can now be done for a remote database
- Column names are now searchable for all tables in database records
- Perform further searches within the results of a previous search
Visualize Your Graph Data More Easily
- Customize the size of data points
- Highlight records from a given filter
- Review large data sets more easily through faster display speed
As always, you can analyze data from other analytical techniques in Luminata. We’ve improved features for these techniques as well:
Processing Hyphenated MS Data with Luminata
Improved Peak Naming for xC/UV/MS Data
Fine-tune peak naming for xC/UV/MS data with new options to:
- Automatically name your peak as a prefix + (optional) number suffix or use selected attributes (i.e., metadata, spectral parameters, etc.)
- Import peak names from your CDS
- Transfer peak names to the Table of Components and keep user-defined names
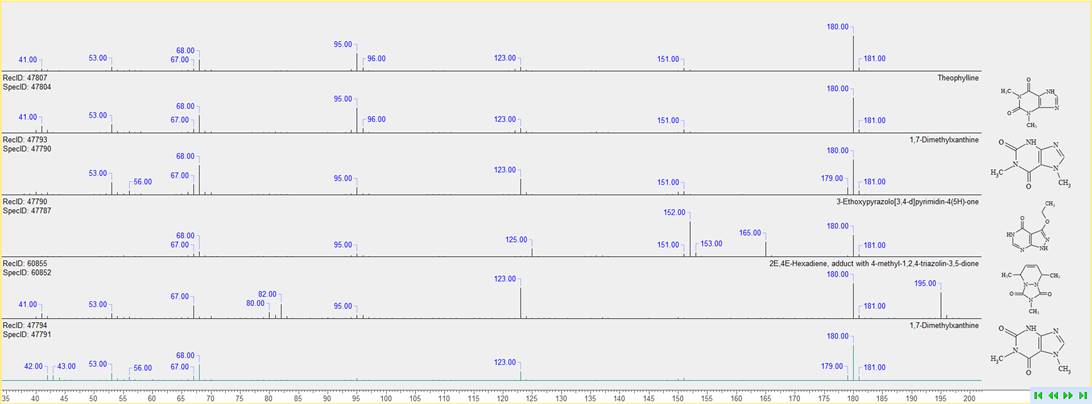
Consolidated Display of Results from Mass Spectral Search
You can now review mass spectral search results more conveniently and find the correct match through concurrent display of the query spectrum with hit spectra, structures, and metadata.
Processing NMR Data with Luminata
Include Integral Assessment in Structure Verification
You can now assess how well the experimental 1H integral values match those predicted for the complete structure using the integral maximum and standard deviations in the Structure User Data table.
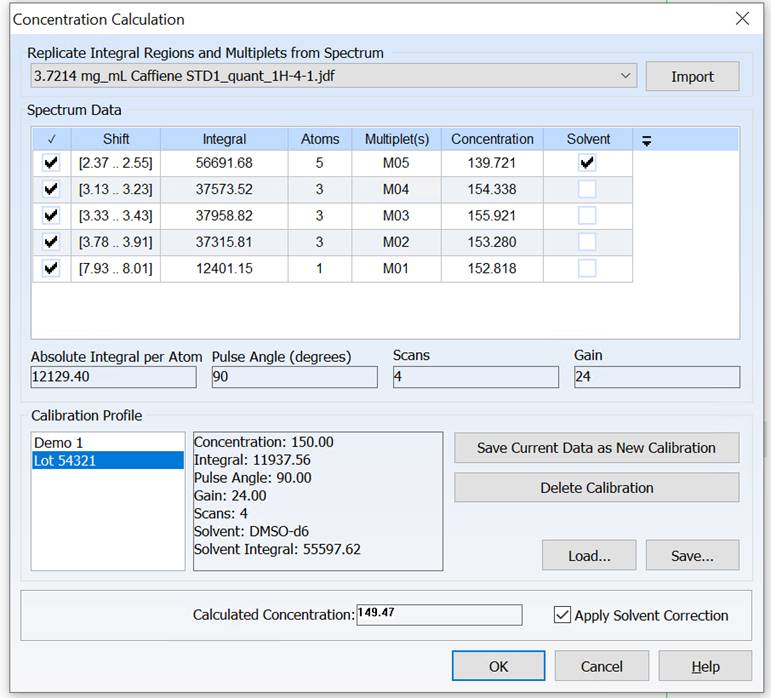
Adjust Solvent Integral to Minimize Error in External Standard qNMR
You can now compensate for error introduced by variability between NMR tubes when using an external standard for qNMR by normalizing the solvent integral in your spectrum with respect to that of the calibration spectrum.