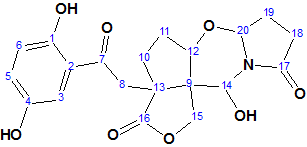
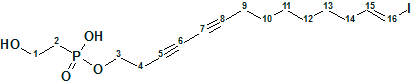
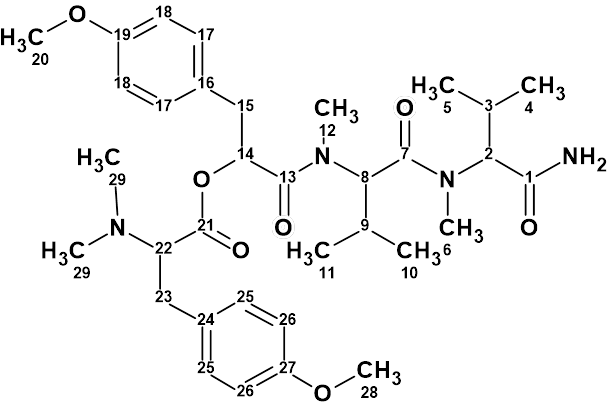
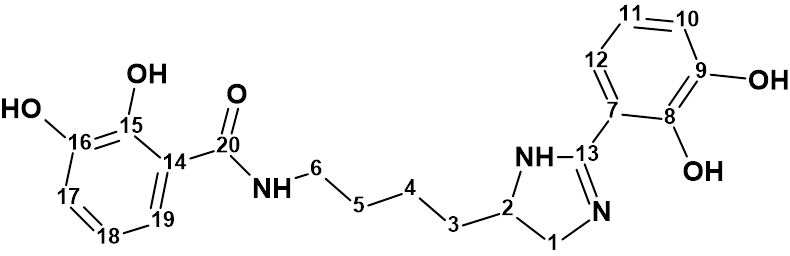
The efficiency of ACD/Structure Elucidator has been confirmed over the years by solving a great number of real world problems (almost 1000) related mainly to the structure determination of new natural products. Over 120 examples are presented in this Elucidation of the Month blog.
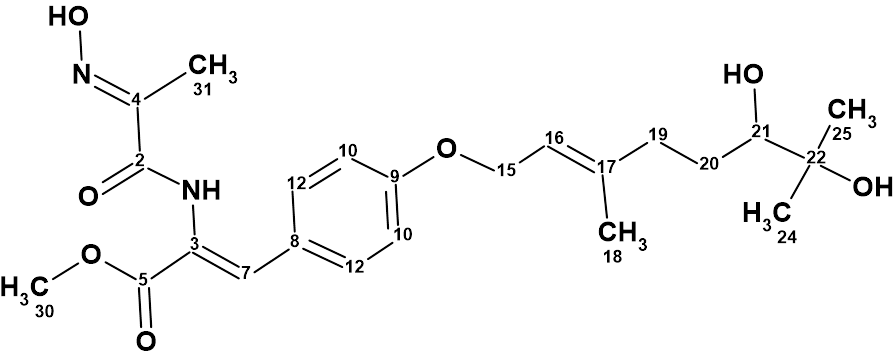
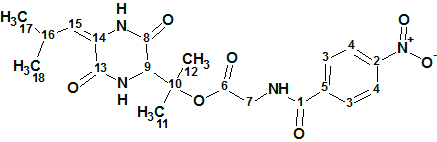
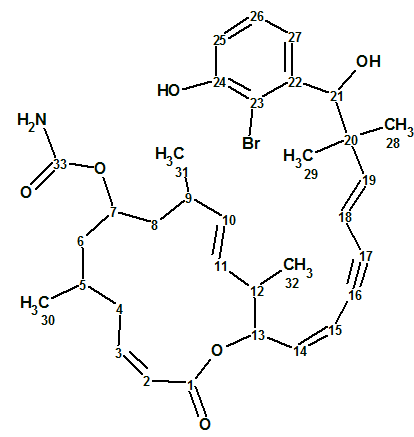
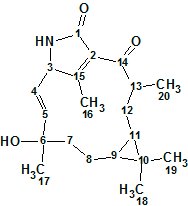
Hectoramide B
The 1H NMR spectrum of Hectoramide B (molecular formula C34H50N4O7) was remarkably similar to that of the previously determined structure of hectoramide A. This posed a difficult structure elucidation, but by introducing minor structural constraints into Structure Elucidator Suite, this challenging problem was solved in a few minutes (in this case using the IR spectrum).
 Read More
Read More
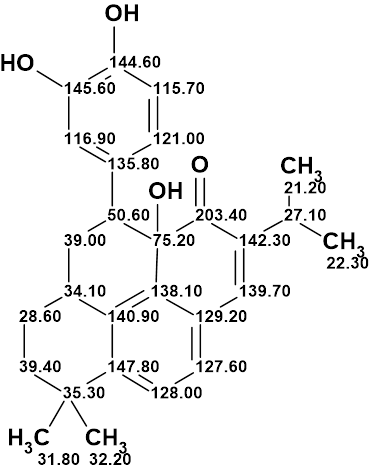
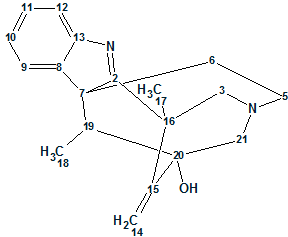
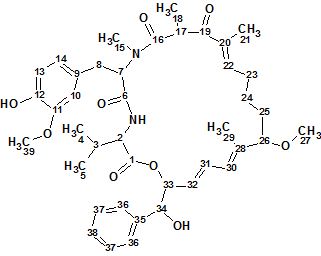
Pseudochelin A
Sonnenschein et al. investigated the fungus Pseudoalteromonas piscicida S2040 to yield pseudochelin A – a new siderophore containing a 4,5-dihydroimidazole moiety. This challenging structure containing eight heteroatoms (three atoms of nitrogen and fife atoms of oxygen) was elucidated by Structure Elucidator fully automatically in 1.5 seconds.
 Read More
Read More
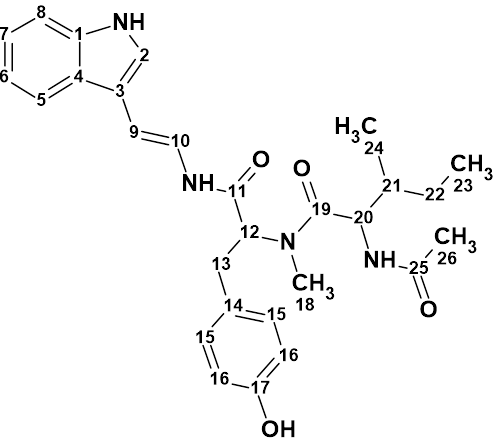
Nordine
Sesquiterpenoids are a class of compounds known to have complex structures, and due to the wide variability of these compounds, it is often challenging to determine the exact structure. Here we discuss the incorrect determination of the structure of Nordine, and later correction; as well as the elucidation of the correct structure using CASE.
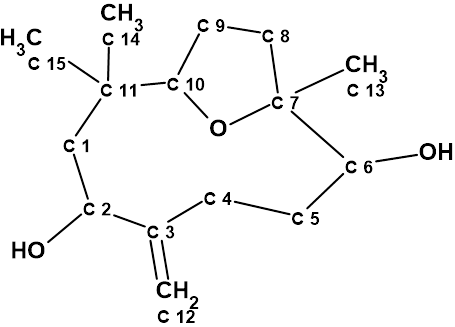 Read More
Read More
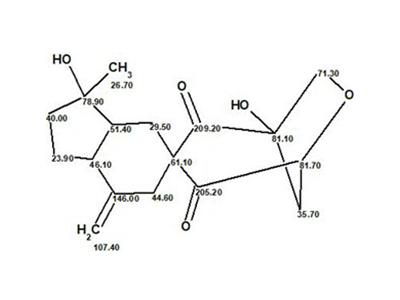
Aspochalasin H1
The structure of aspochalasin H1 (molecular formula C24H35NO5) was elucidated using 1D and 2D NMR, high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy, and comparisons with the reported literature. The CASE-based structure elucidation was carried out by Structure Elucidator Suite in half a minute.
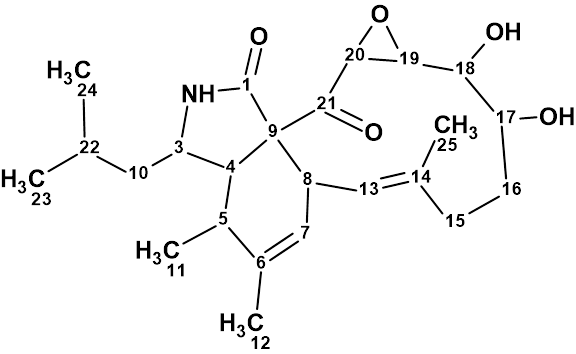 Read More
Read More
Plebeianiol A
Many corrections of erroneous structures published in the literature have been made with the help of Structure Elucidator Suite. In this example, we were interested to know what the result of using Structure Elucidator for the revision of the plebeianiol A structure would be if the NMR data presented in the work of Liang and collaborators were used.
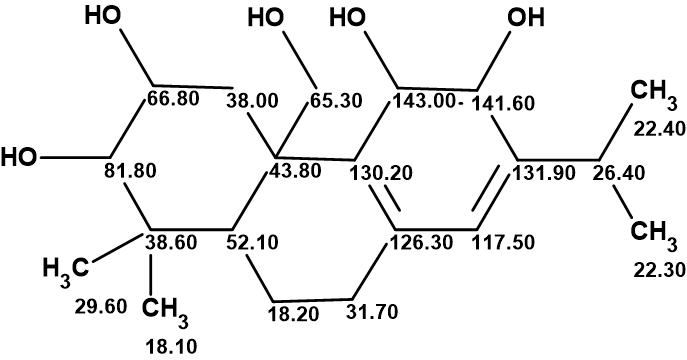 Read More
Read More
Saccharobisindole
Analysis of the chemical components of the marine bacterium Saccharomonospora sp. CNQ-490 carried out by Fenical and coworkers yielded three novel compounds, including saccharobisindole (molecular formula C26H28N2O3). Its chemical structure was elucidated by the interpretation of 1D, 2D NMR (HSQC, HMBC and COSY), and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS) data.
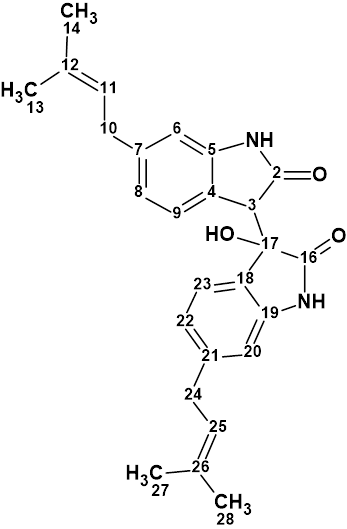 Read More
Read More
Rumphellol A
Sung et al. isolated two new caryophyllene-type sesquiterpenoids, rumphellol A and B, from the Rumphella antipathies gorgorian coral. These compounds contain a 9-membered ring fused with a cyclobutane ring, which is rarely observed in natural products. We used ACD/Structure Elucidator to confirm the structure of rumphellol A (molecular formula C15H24O2).
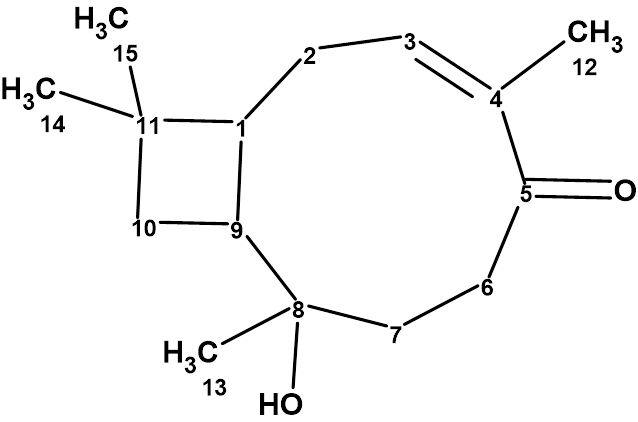 Read More
Read More
Trichopsistide A
Using the traditional method of structure elucidation based on analysis of HSQC, HMBC and COSY data, the authors deduced a large part of the molecular structure, but the lack of carbons bearing hydrogen atoms prevented them to assemble the full structure. To alleviate this problem, ACD/Structure Elucidator was utilized in Trichopsistide A, molecular formula C23H29NO5.
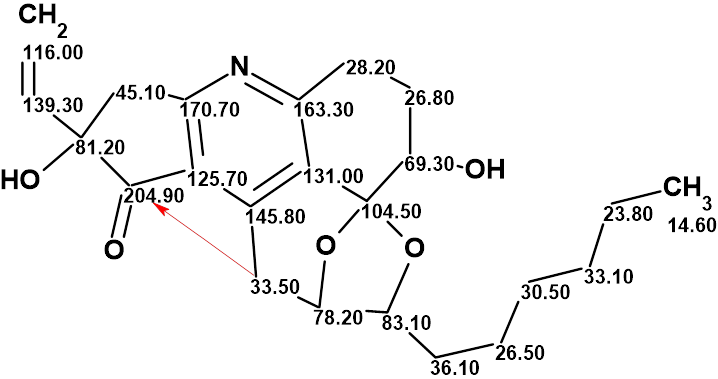 Read More
Read More
Dichocetide D
Shaker et al. recently reported the isolation of Dichocetide D from the marine fungus Dichotomomyces cejpii under oxygen stress conditions. The structure of Dichocetide D was revised by Elyashberg et al on the basis of chemical considerations and utilization of ACD/Structure Elucidator.
 Read More
Read More
Vagiallene
E. Ioannou et al have developed an integrated metabolomic platform for the identification of known compounds and detection of new metabolites at the early stages of phytochemical analysis. Vagiallene was isolated through a series of chromatographic separations, molecular formula C15H15Br2O5.
 Read More
Read More
Spiroaxillarone A
Spirobisnaphthalenes are a relatively new and rare family of secondary metabolites. Their core structure usually consists of two bicyclo[4.4.0]decane units, connected with one another through at least one spiro center. The reported compound is a novel symmetric spirobisnaphthalene with a unique structural feature. Spiroaxillarone A, molecular formula C19H12O6.
 Read More
Read More
Chloraserrtone A Structure Elucidation
Chloraserrtone A, a new sesquiterpenoid dimer with two lindenane-type sesquiterpenoid monomers bridged by two six-membered rings, was isolated from Chloranthus serratus by Bai et al. It represents the first lindenane-type sesquiterpenoid dimer with an extremely unique skeleton, molecular formula C3H36O9.
 Read More
Read More
Synthetic product C14H13N3O Structure Elucidation
An unexpected synthetic product coming from Leibniz-Forschungsinstitut für Molekulare Pharmakologie (FMP) in Berlin, from the lab of Dr. Marc Nazaré. The dataset was provided to ACD/Labs as part of our Structure Elucidation Suite Challenge. The product was isolated after a reaction and it was found by HR-MS to have a molecular formula of C14H13N3O.
 Read More
Read More
Penerpene A Structure Elucidation
The Penicillium sp. KFS28 fungus was isolated from a bivalve mollusk, Meretrix Lusoria, from the Haikou Bay in China. The EtOAc extract of the fermentation broth was processed by the authors who isolated and identified four new paxilline-type indole-terpenoids. Compound 1 has the molecular formula C28H35NO6.
 Read More
Read More
Ent-Kaurane-Type Diterpenoid Structure Elucidation
Yaouba et al reported the isolation and phytochemical investigation of the constituents of Aspilia pluriseta Schweinf and Aspilia mossambicensis. They isolated, identified and comprehensively investigated compound 1, molecular formula C21H30O3.
 Read More
Read More
Neosetophomone A Structure Elucidation
El-Elimat et al reported five new and one known meroterpenoids, including the discovery of a novel ioxa[4.3.3]propellane metabolite neosetophomone A that incorporates a 3-methyl-2,3-dihydrofuran bridge into a 5,6 tricyclic 2-hydroxycyclopent-2-en-1-one/tetrahydropyran ring system, molecular formula C24H32O5.
 Read More
Read More
5α-Cyprinol Structure Elucidation
5α-cyprinol sulfate was isolated from a methanolic extract of fish bile (Cyprinus carpio) after separation by preparative LC. The molecular mass and the presence of a sulfate group were revealed by ESI–MS/MS in the negative mode, and the molecular formula of the compound was determined as C27H48O8S.
 Read More
Read More
Cycloshermilamine D Structure Elucidation
Investigation of Cystodytes resulted in the isolation of five pyridoacridines, including shermilamines D and E. The structure of another compound, cycloshermilamine D, also isolated from the same tunicate in minute amounts (0.4% of the crude extract) was determined by Koren-Goldshlager et al, molecular formula C21H16N4OS.
 Read More
Read More
Oroidin Structure Elucidation
Oroidin (C11H10Br2N4O) is a highly proton-deficient bromopyrrole isolated from the sponge Agelas oroides. A CASE solution to this problem was chosen for testing the capability of DFT based NMR chemical shift prediction to distinguish the correct structure when empirical prediction methods fail to suggest the structure reliably.
 Read More
Read More
Uncarilin A
In the search for novel MT receptor agonists from natural sources, Geng at al used LC-MS to study U. rhynchophylla,, resulting in the isolation of two pairs of dimeric isoechinulin-type enantiomers, (±)-uncarilin A and (±)-uncarilin B. Here we discuss the structure elucidation of uncarilin A (molecular formula C38H42N6O4).
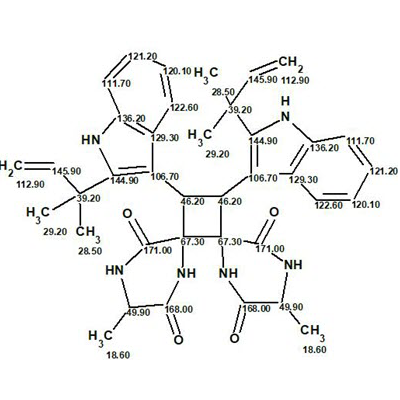 Read More
Read More
Matsutakone – Pleurocin A
The ethyl acetate layer of T. matsutake was fractionated and purified by repeated chromatographic methods to yield the white powder matsutakone, molecular formula C28H44O4. The structure of Structure of matsutakone was elucidated from its molecular formula and 1D and 2D NMR data shown in Table 1, which were used by us for challenging ACD/Structure Elucidator.
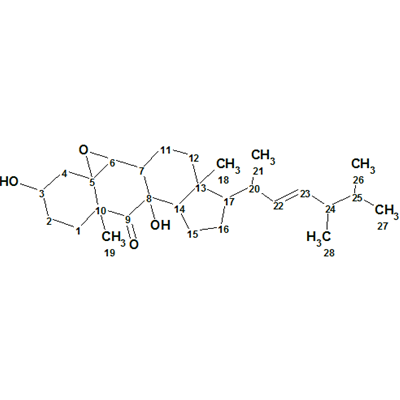 Read More
Read More
Emodacidamide A
During screenings for new secondary metabolites from fungi originating from the South China Sea, Luo and co-workers isolated 10 anthraquinone compounds, including eight new anthraquinones regarded as emodacidamides A−H. Structures of these compounds were elucidated, and the NMR data utilized for the structure elucidation of emodacidamide A (molecular formula C21H19NO8) were used by us to challenge ACD/Structure Elucidator.
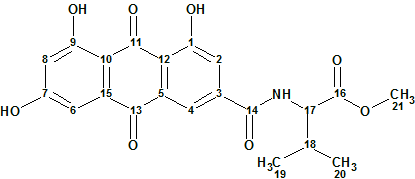 Read More
Read More
Abyssomicin W
Wang et al. reported the discovery of 12 new analogs of abyssomicin as metabolites of the Streptomyces species. Amongst them Abyssomicin W (molecular formula C20H26O8) has an 8/6/6/6 tetracyclic core. Spectroscopic data of this compound were used to challenge ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite.
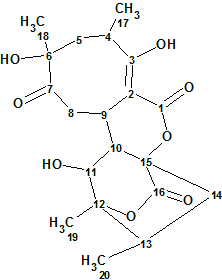 Read More
Read More
Trichoderpyrone
Chen et al have been looking for novel secondary metabolites from Trichoderma gamsii, a plant endophytic fungus. As a result of this a new polyketide trichoderpyrone (molecular formula C15H17NO5), containing a unique cyclopentenone−pyrone hybrid skeleton was isolated and its structure was determined by detailed analysis of NMR data.
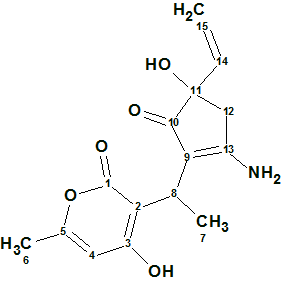 Read More
Read More
Spiroschincarin A
Song et al investigated the chemical constituents of the fruit of S. incarnata. They isolated five novel spirocyclic compounds, spiroschincarins A−E, featuring a unique 1-oxaspiro[6.6]tridecane moiety. Their structures, with absolute configurations, were determined by extensive spectroscopic studies. The structure elucidation of spiroschincarin A (molecular formula C31H38O11) from NMR data was used for challenging ACD/Structure Elucidator.
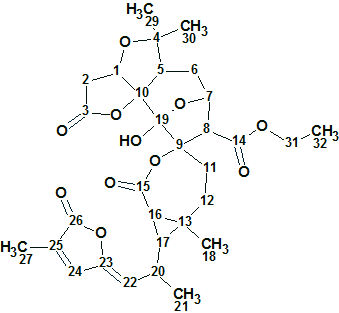 Read More
Read More
Sophaline C
Y.-B. Zhang and co-workers reported four novel matrine-based alkaloids, sophalines A-D. Their structures were elucidated using spectroscopic methods and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. We used the Spectroscopic data for Sophaline C (molecular formula C21H26N2O2) to challenge Structure Elucidator.
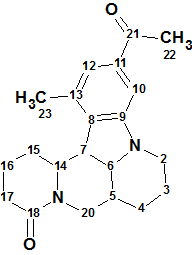 Read More
Read More
4-Bromobenzoic-biscognienyne A
4-Bromobenzoic-biscognienyne A (molecular formula C23H25O4Br) is relatively simple but its elucidation was chosen as a demonstrated approach, using ACD/Structure Elucidator, in situations where several equiprobable user assumptions (“axioms”) should be checked to determine the right structure.
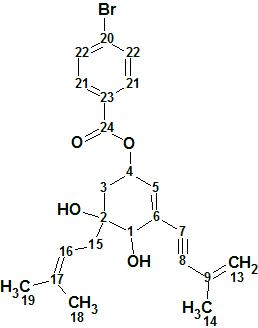 Read More
Read More
Alistonitrine A
Monoterpene Indole Alkaloids (MIAs) are found in Alstonia scholaris R. Br. (Apocynaceae) which originates in South Asia. People in the area have been using the bark and leaves as traditional medicines. Zhu and co-workers successfully isolated a new MIA, Alistonitrine A (molecular formula C21H25N3O3), which possesses an unprecedented caged monoterpene indole skeleton.
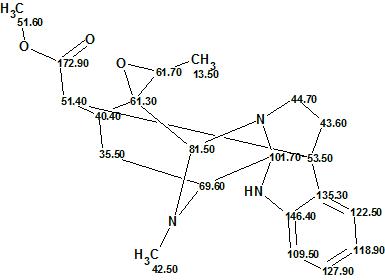 Read More
Read More
Euphorikanin A
Fei and co-workers4 isolated Euphorikanin A (molecular formula C20H26O3), a structurally novel diterpenoid lactone with an unprecedented carbon skeleton featuring a unique tetradecahydrobenzo[cd]-cyclopropa[f ]azulene. Its structure was determined by spectroscopic methods and confirmed by single crystal X-ray analysis.
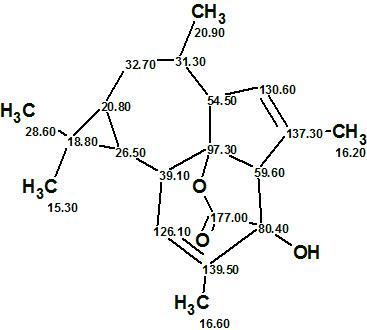 Read More
Read More
Ciliatonoid A
Structures of ciliatonoids A-C, complete with absolute stereochemistry, were characterized by spectroscopic data, X-ray crystallography, and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) analysis. To challenge ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite, Ciliatonoid A (molecular formula C26H32O5) was used. It featured an unprecedented limonoid architecture by way of a very unique cis-fused central motif (in red).
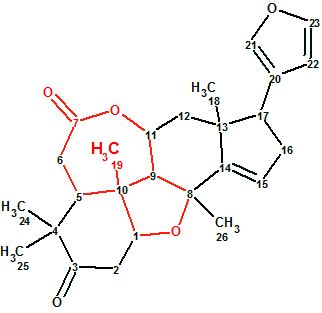 Read More
Read More
Pepluacetal
Wan et al isolated and identified three highly modified and biogenetically related diterpenoids including Pepluacetal (molecular formula C22H32O4), which has a novel unprecedented fused-ring skeleton containing cyclopentane and cyclobutane rings which rarely occur in natural compounds.
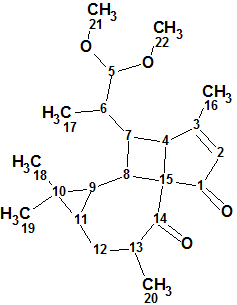 Read More
Read More
Flueggether A
H. Zhang et al observed interesting signals from very minor constituents from F. virosa in their MS analysis. A further fractionation of the fractions returned two extra new alkaloids, one of which, Flueggether A(molecular formula C25H30N2O5), is the first example of Securinega alkaloid oligomers which features an ether bond linkage.
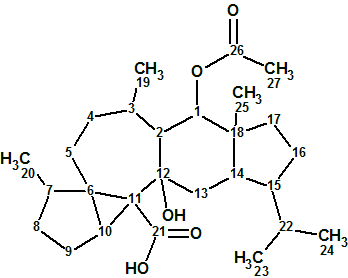 Read More
Read More
Astellifadiene
The authors reported the production and structure characterization of the novel sesterterpene Astellifadiene. Analysis of the 1H-1H COSY, HMBC, and NOESY correlations established the planar structure as an unprecedented 6-8-6-5-membered tetracyclic ring system. The use of NMR analyses combined with the crystalline sponge method facilitated the unambiguous determination of the Astellifadiene structure (molecular formula C25H40).
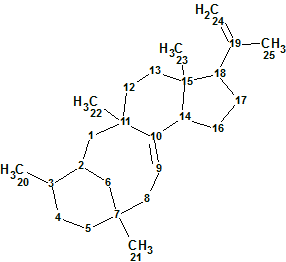 Read More
Read More
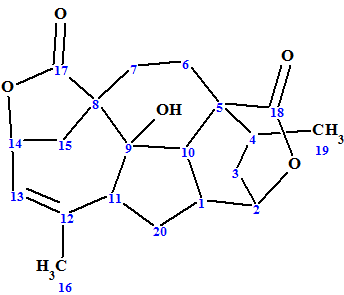
Mannolide A
Ni et al investigated Cephalotaxus mannii Hook f. which led to the isolation of three new diterpenoids, namely, mannolides A−C, and two new Cephalotaxus troponoids. We used the example of Mannolide A (molecular formula C20H24O5) to challenge our ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite software.
 Read More
Read More
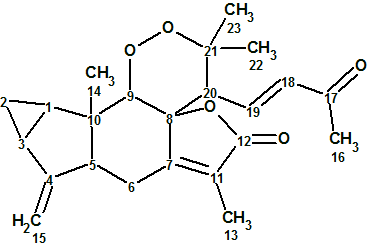
Sarglaperoxide A
From investigating the constituents of Sarcandra glabra, P. Wang et al isolated a pair of structurally-related terpene lactones, sarglaperoxides A and B. The original experimental data related to Sarglaperoxide A (molecular formula C23H28O5) were used to challenge ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite and determine if the software could reliably elucidate this novel structure.
 Read More
Read More
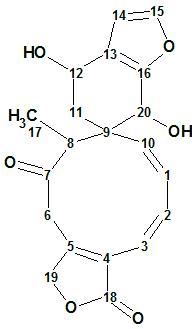
Teotihuacanin
Bautista et al reinvestigated the chemical composition of S. amarissima. As a result, Teotihuacanin (molecular formula C20H20O6), an unusual rearranged clerodane diterpene with a new carbon skeleton containing a spiro-10/6 bicyclic system, was isolated from the leaves and flowers of Salvia amarissima.
 Read More
Read More
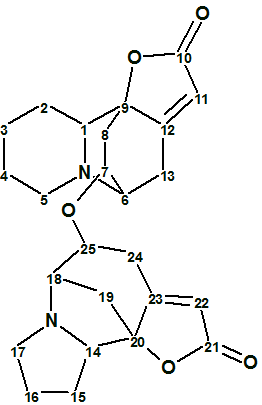
Flueggether A
H. Zhang et al observed interesting signals from very minor constituents from F. virosa in their MS analysis. A further fractionation of the fractions showing the interesting MS peaks returned two extra new alkaloids, one of which, Flueggether A (molecular formula C25H30N2O5) is the first example of Securinega alkaloid oligomers which features an ether bond linkage.
 Read More
Read More
Tronoharine
Tronoharine was isolated in a small amount as a minor alkaloid from a sample of T. corymbosa and given a proposed structure. In a more recent work, it was obtained in a more significant amount, which enabled the authors to reevaluate the previously proposed structure. Structure Elucidator Suite was used to confirm the newly proposed structure of Tronoharine ((molecular formula C21H24N2O2).
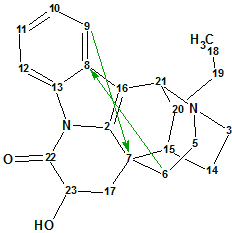 Read More
Read More
Spirochensilide A
Zhao et al isolated two novel rearranged triterpenoids from the leaves and twigs of A. chensiensis.—Spirochensilides A and B. The spectroscopic data used to elucidate the structure of Spirochensilide A (molecular formula C30H42O5), a compound containing unprecedented spiro-[5,6]system, were used to challenge ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite.
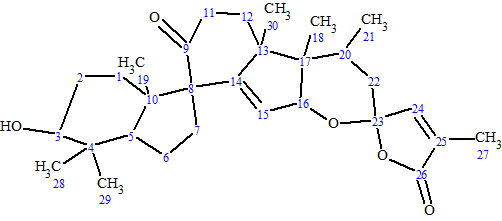 Read More
Read More
A Heterodimer from P. kaurabassana
Two heterodimers comprising an anthraquinone moiety linked to a 3-methylbenzodihydroisocoumarin unit were isolated from P. kaurabassana tubers. The NMR spectroscopic data presented therein were used by us to challenge the ACD/Structure Elucidator system, by attempting to successfully elucidate structure 1 (molecular formula C31H24O10).
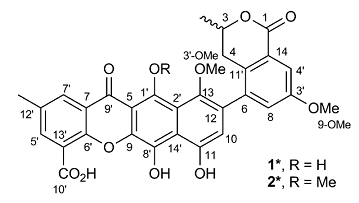 Read More
Read More
Garcimulin A
Fan et al isolated two PPAPs, Garcimulins A and B, including a pair of enantiomers [(+)-Garcimulin A and (-)-Garcimulin A)] with the unique caged tetracyclo[5.4.1.11,5.09,13]tridecane skeleton from the leaves and twigs of G. multiflora. The spectroscopic 1D and 2D NMR data used by the authors for structure elucidation of Garcimulin A (molecular formula C38H50O6) were input into ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite.
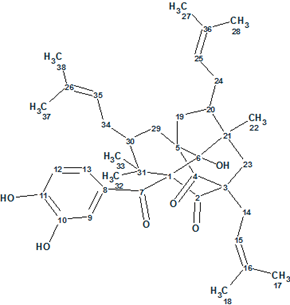 Read More
Read More
Bacillusin A
R.R. Ravu and coworkers performed work searching for new antibiotics against drug-resistant bacteria. Preliminary fractionation of the crude extracts of the B. amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum strain AP183 afforded activity-enriched fractions that contained an apparently unknown active compound with strong UV absorptions. A scale-up fermentation of this Bacillus strain was conducted, leading to the isolation and identification of Bacillusin A (molecular formula C68H92O18).
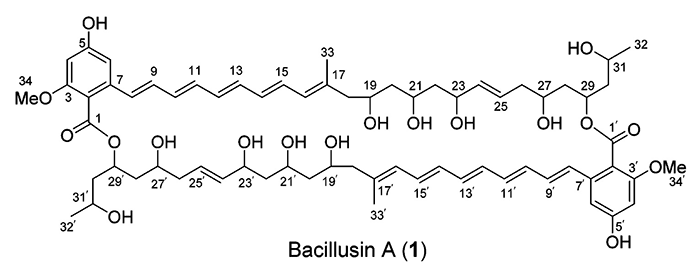 Read More
Read More
Laevinoid A
Wang and coworkers collected the branches and leaves of Croton laevigatus and performed an intensive chemical analysis. They isolated and elucidated structures of two diterpenoids, laevinoids A (molecular formula C20H22O5) and B, which represent a new rearranged ent-clerodane scaffold with an unusual 3/5 bicyclic motif.
 Read More
Read More
Virosaine
Zhao and co-workers isolated two new Securinega alkaloids (virosaines A and B) with an unprecedented skeleton and elucidated their structures. We used the spectroscopic data presented in by the authors to establish the structure of Virosaine A (molecular formula C12H13NO4) which had been confirmed by X-ray diffraction.
 Read More
Read More
Schiglautone A
Meng et al. investigated potentially biologically active substances from the chemical constituents of the stems of S. glaucescens. As a result, a novel triterpenoid possessing an unusual 6/7/9-fused tricyclic ring system was obtained, which was designated as Schiglautone A (molecular formula C30H46O6).
 Read More
Read More
Puberunine
While studying the herb Aconitum barbatum Pers. var. puberulum Ledeb., Mu et al isolated six new C18-diterpenoid alkaloids including Puberunine (molecular formula C23H35NO7) that possesses an unusual rearranged 7-membered ring. This structural feature is unprecedented in the field of diterpenoid alkaloids.
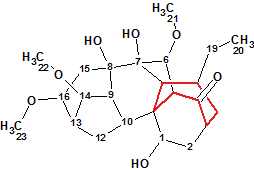 Read More
Read More
Strynuxline A
Studies aimed at the discovery of trace alkaloids in S. nux-vomica led Fu and co-workers to the isolation of Strynuxlines A and B, two novel alkaloids possessing an unprecedented skeleton with a 6/5/9/6/7/6 hexacyclic ring system. Here we will describe how Strynuxlines A (molecular formula C23H24N2O5) could be identified with the assistance of a CASE-based approach using ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite.
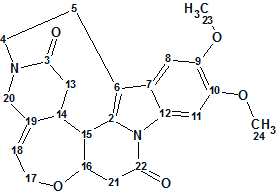 Read More
Read More
Strophasterol A
In search for bioactive compounds from the mushroom Stropharia rugosoannulata, Wu et al discovered four novel steroids named strophasterols A, B, C, and D which contained a very unique and unprecedented carbon skeleton. Here we will describe the computerized structure determination of Strophasterol A (molecular formula C28H44O4).
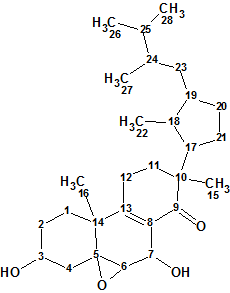 Read More
Read More
Acremolin
Here we describe a total synthesis of a hypothetical alternative structure and its spectroscopic confirmation, representing a huge amount of work done by the authors to disprove the original structure. We used their example to ask what solution would be obtained if the authors used ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite for processing the spectroscopic data of the unknown.
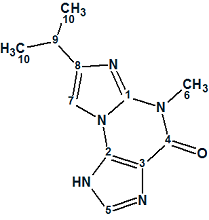 Read More
Read More
Trigoflavidol A
Tang et al carried out a phytochemical investigation on the stems of T. flavidus collected in China. They reported the identification of five degraded diterpenoids, including the tetranorditerpenoid dimers trigoflavidols A and B. Spectroscopic data acquired for Trigoflavidol A (molecular formula C35H32O10), possessing a rearrangement skeleton with a spiroketal core moiety, was used for challenging ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite.
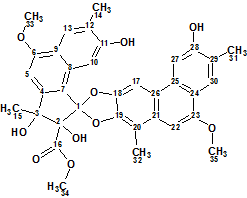 Read More
Read More
Gymnopalyne A
In searching for novel antibiotics, Thongbai et al have focused on tropical basidiomycetes from Asia. The research led to the isolation of unprecedented antimicrobial metabolite Gymnopalynes A (molecular formula C12H7O2Cl). Though the molecule is small and relatively simple, elucidation of its structure is not straightforward. With this in mind we used this problem to illustrate some nuances associated with utilization of ACD/Structure Elucidation.
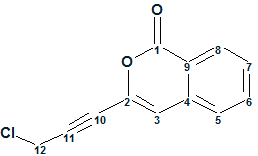 Read More
Read More
Mandelalide A
Sikorska et al isolated and investigated the unusual polyketide macrolides Mandelalides A-D which were isolated from a new species of Lissoclinum ascidian. Their planar structures were elucidated from sub-milligram samples by comprehensive analysis of 1D and 2D NMR data, and supported by mass spectrometry. Here we will describe the elucidation of Mandelalide A (molecular formula C33H52O11) using ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite.
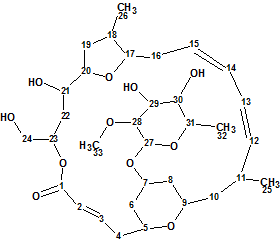 Read More
Read More
TAEMC161 (Viridol)
This example clearly shows how an improper axiom assumption by a researcher can lead to an incorrect structure. Employing an unbiased analysis of spectral data using Structure Elucidator Suite would allow the authors to infer the correct structure (Viridol, molecular formula C20H18O6) unambiguously in several seconds.
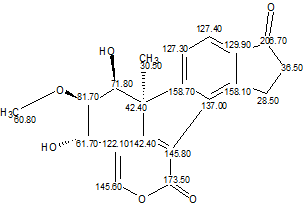 Read More
Read More
Barmumycin
Lorente and co-workers isolated two known compounds, pretomaymycin and oxotomaymycin, plus the previously unknown compound barmumycin from the culture broth of the marine actinomycete Streptomyces sp. BOSC-022A. Barmumycin (molecular formula C15H19NO4)and its diacetate show antitumor activity at micromolar concentrations.
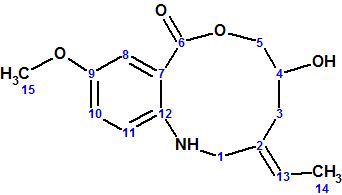 Read More
Read More
Schizocommunin
A reinvestigation of the NMR and IR results for natural schizocommunin led the researchers to propose a revised structure, quinazolinone. We suggested that if a CASE approach were used elucidate the structure when this compound was firstly isolated, the structure revision would be not necessary: for final structure confirmation X-ray crystallographic analysis would be sufficient.
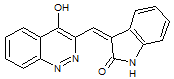 Read More
Read More
Epohelmin A
This month we re-visit the example of structure revision of Epohelmin A with structure revision utilizing ACD/Structure Elucidator Suite, which demonstrates how the software allows a researcher to avoid complex multi-stage synthesis to refute a wrong proposed structure and prove the revised one.
Read MoreAscidia sydneiensis SAAF
To understand the molecular mechanism underlying the genus-specificity of ascidians’ sperm chemotaxis, Matsumori et al investigated the structure of a novel compound Ascidia-SAAF 2 (molecular formula C27H44O10S2Na2), which was isolated from the eggs of the ascidian Ascidia sydneiensis. Utilizing Structure Elucidator Suite allowed the correct structure of unknown, and its configuration upon a double bond to be determined.
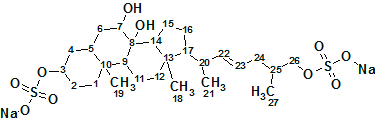 Read More
Read More
Aquatolide
Aquatolide is a humulane-derived sesquiterpenoid lactone isolated from Asteriscus aquaticus. The structure originally proposed on the basis of 1D and 2D NMR analysis contains an exceedingly rare ladderane substructure. As a result of the quantum-chemical (QM) calculations of the 13C and 1H chemical shifts and associated coupling constants for a series of possible structures, it was shown that the proposed structure was incorrect. We applied a well-established Computer Assisted Structure Elucidation (CASE) method to the problem, in order to compare results with the QM method.
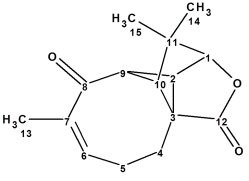 Read More
Read More
Asidia SAAF
To understand the molecular mechanism underlying the genus-specificity of sperm chemotaxis of ascidians (a type of marine invertebrate filter feeders), Matsumori et al have investigated the structure of a novel compound Ascidia-SAAF 2 (molecular formula C27H44O10S2Na2) isolated from the eggs of the ascidian Ascidia sydneiensis.
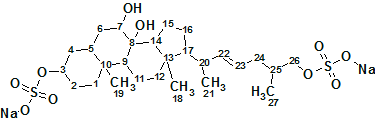 Read More
Read More
Polypropionat
Marine mollusks of the genus Siphonaria, commonly known as false limpets, are shelled, air-breathing herbivores that are believed to have a marine ancestry. When disturbed, siphonariid limpets secrete a sticky white mucus rich in polypropionate secondary metabolites. Specimens were steeped in acetone, and the acetone extract was subjected to extensive chromatography to afford three new polypropionate metabolites. Spectroscopic data of Polypropionate 1 (molecular formula C20H32O3) are used here to describe the structure elucidation of this compound using CASE techniques.
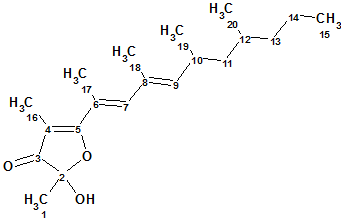 Read More
Read More
Geralcin A
Le Goff et al reported the structural characterization of two novel alkylhydrazides produced by the bacterial strain Streptomyces sp. LMA-545. The structures were elucidated using 1D and 2D 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopic analysis and high-resolution mass spectrometry. 1H–15N NMR experiments were required for full structural elucidation. Here we investigate the structure elucidation of Geralcin A ( molecular formula C15H24N2O5), one of the three isolated novel compounds.
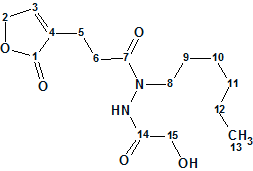 Read More
Read More
Protuboxepin A
Lee et al have investigated the chemical constituents of the extracts obtained from cultures of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SF-5044. This study led to the isolation of new natural products, particularly, an oxepin-containing diketopiperazine-type metabolite named Protuboxepins A (molecular formula C22H23N3O3).
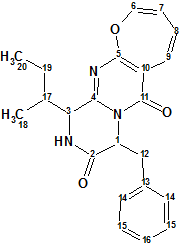 Read More
Read More
Lycojaponicumin D
Previously Wang et al reported three trace Lycopodium alkaloids, lycojaponicumins A and B with a 5/5/5/5/6 pentacyclic ring system and lycojaponicumin C with a 6/5/5/6 tetracyclic ring system. The same group later described the discovery of structurally unique alkaloid, Lycojaponicumin D (molecular formula was established to be C16H23NO3), with an unprecedented 5/7/6/6 tetracyclic skeleton formed by an unusual C3-C13 linkage.
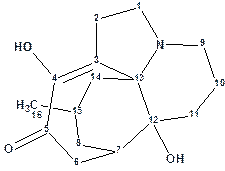 Read More
Read More
Indol alkaloid
An aqueous extract of the roots of I. indigotica has been investigated by Chen and co-workers. In this work, the authors isolated and structurally characterized an indole alkaloid containing unusual dihydrothiopyran and 1,2,4-thiadiazole rings (molecular formula C18H17N3O2S2).
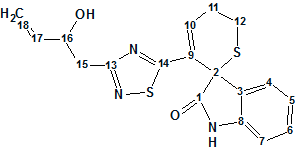 Read More
Read More
Asperjinone
Liao et al isolated and elucidated the structure of a new natural product named as Asperjinone (molecular formula C22H20O6). Our analysis using ACD/Structure Elucidator resulted in the revision of the structure. The story of the structure revision is described in the Journal of Natural Products.
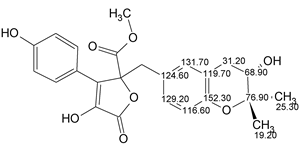 Read More
Read More
Geranylphenazinediol
Ohlendorf and co-workers describe isolation and structure elucidation of Geranylphenazinediol (molecular formula C22H24N2O2), a phenazinediol substituted with an isoprenoid side chain. We used ACD/Structure Elucidator to elucidate structure of this new natural product using only its NMR spectroscopic data.
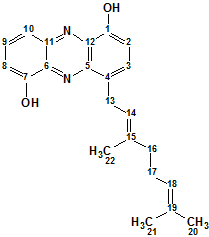 Read More
Read More
Lasionectrin
El Aouad at al isolated a new naphthopyrone (structure 1) named Lasionectrin (molecular formula C19H20O6) with antiplasmodial properties from fermentation broths of a Lasionectria species. The article constitutes the first account on the isolation of a natural product from fungi of this genus.
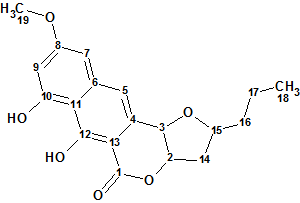 Read More
Read More
Daphmacromine A
M. Cao and co-workers described the isolation and structure elucidation of 10 new alkaloids belonging to the Daphniphyllum alkaloids family. The spectral data presented for one of the compounds, Daphmacromine A (molecular formula C25H37NO5), were used to challenge ACD/Structure Elucidator.
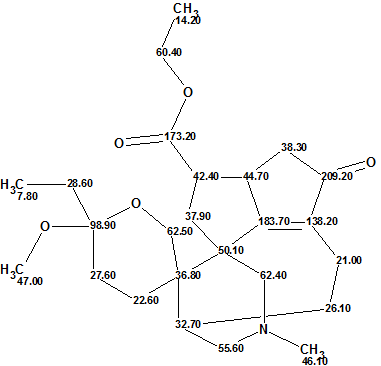 Read More
Read More
Lycojaponicumin
Wang et al isolated a novel alkaloid lycojaponicumin (molecular formula C16H21NO4) from the alkaloidal extract in a trace amount, with a unique 5/5/5/5/6 pentacyclic ring system including two fused tetrahydroisoxazole rings. The structure was elucidated by spectroscopic methods and X-ray diffraction analysis.
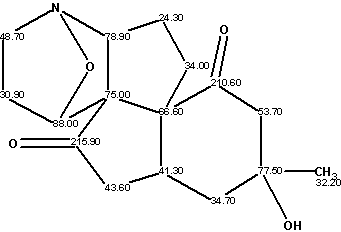 Read More
Read More
Psychotripine
A recent article highlighted the isolation and structure elucidation of a new natural product Psychotripine (molecular formula C33H34N6), which exhibited a complex carbon skeleton comprised of 11 rings. We attempted the Computer-Assisted Structure Elucidation (CASE) of Psychotriptine using only the original limited and incomplete NMR data gathered from the original publication
 Read More
Read More
Tasiamide B
Philip Williams and co-workers isolated a new cytotoxic peptide, Tasiamide B (molecular formula C50H74N8O12) containing the unusual amino acid-derived residue 4-amino-3-hydroxy-5-phenylpentanoic acid. The structure of the peptide was determined through a combination of 2D NMR experiments and HPLC analysis of degradation products. The experimental data was submitted to the Structure Elucidator Challenge to determine if the software could propose the same structure.
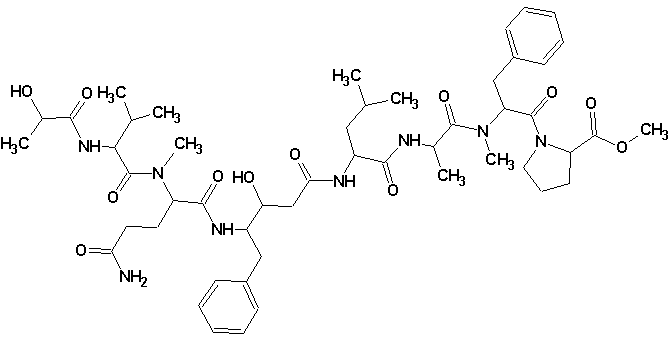 Read More
Read More
Phoriospongin A
Robert Capon and co-workers identified two new nematocidal depsipeptides, identified as phoriospongins A (molecular formula C52H82N11O15Cl) and B. The structures of the phoriospongins were determined by detailed spectroscopic analysis and comparison with the previously reported sponge depsipeptide cyclolithistide A. The experimental data was submitted to the Structure Elucidator Challenge to determine if the software could propose the same structure.
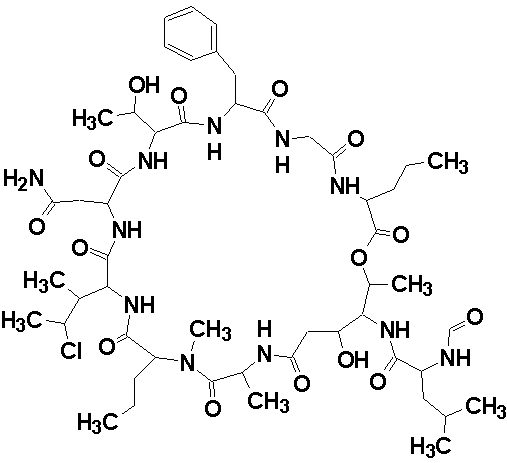 Read More
Read More
α-botryoxanthin A
Botryococcus braunii is a colonial green microalga that is known for producing various types of hydrocarbons and other types of oils. In a 1998 publication, Okada and co-workers isolated and identified two new carotenoids in their efforts to better understand the relationship between colony color and hydrocarbon production, one of which was α-botryoxanthin A (molecular formula C74H112O2).
Read MoreExample Elucidation
For more than a decade, ACD/Structure Elucidator has been used by industry and academic experts to help solve some of the toughest structure problems. Using data from various analytical techniques (NMR, MS, UV, and IR) Structure Elucidator can propose chemical structures that are consistent with ALL available analytical data.
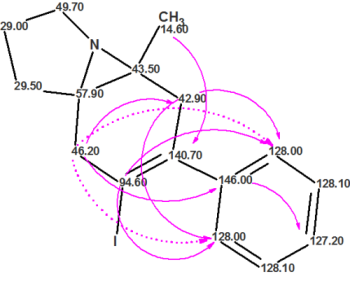 Read More
Read More